Introduction
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSSs) are increasingly vital in modern healthcare, acting as essential tools for clinicians to enhance patient care, minimize medical errors, and boost clinical efficiency. By delivering evidence-based recommendations at the point of care, CDSSs aim to improve decision-making processes in complex medical environments. These systems represent a significant evolution in how medical professionals utilize data and technology, yet their full potential remains somewhat untapped due to various implementation challenges. Like the precision required in China Health Care Device Parts Tooling, the development and deployment of effective CDSS demand meticulous attention to detail and robust infrastructure. This review explores the current landscape of CDSS, examining their evolution, implementation hurdles, benefits, limitations, and future trajectories, while also drawing parallels to the critical precision found in fields like china health care device parts tooling to highlight the need for accuracy and reliability in healthcare technology. We will also consider how advancements in related industries, such as those involved in china health care device parts tooling, can inform and inspire improvements in CDSS design and functionality.
Current State of CDSS
History of CDSS
The journey of CDSSs from rudimentary rule-based systems to sophisticated AI-driven tools marks a significant transformation in healthcare technology. Understanding this historical progression is crucial to appreciating the current capabilities and future potential of CDSS.
From their inception, CDSSs have mirrored advancements in computing and artificial intelligence. Early concepts emerged in the late 1950s, with pioneers like Ledley and Lusted envisioning computers aiding medical diagnosis. This foundational work laid the groundwork for subsequent developments.
Early Beginnings (1950s–1960s)
The late 1950s witnessed the birth of CDSS concepts with the introduction of computers into medical thinking. Ledley and Lusted’s groundbreaking paper, ‘Reasoning Foundations of Medical Diagnosis,’ proposed using computers for medical decision-making, a concept as novel and potentially impactful as early innovations in china health care device parts tooling were for manufacturing.
Early Expert Systems (1970s–1980s)
The 1970s and 1980s saw the rise of expert systems utilizing AI. MYCIN, designed for antibiotic selection, and INTERNIST-1, aimed at diagnosing complex cases, exemplified this era. These systems, much like early automated machinery reliant on precise china health care device parts tooling, were rule-based, encoding expert medical knowledge into ‘if-then’ rules.
Integration with EHRs (1990s–2000s)
The widespread adoption of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) in the 1990s and 2000s spurred the integration of CDSSs with EHRs. This integration was crucial, enabling CDSSs to provide patient-specific recommendations by accessing real-time data. Standards like Health Level Seven facilitated data exchange, mirroring the standardization efforts in china health care device parts tooling to ensure compatibility and efficiency.
The Rise of Evidence-Based Medicine (Late 1990s–2000s)
The late 1990s emphasized evidence-based medicine, promoting clinical decisions informed by the best available research. This shift drove the development of CDSSs incorporating evidence-based guidelines, helping clinicians make decisions grounded in the latest scientific findings, much like quality control in china health care device parts tooling relies on empirical testing and data.
Advancements in AI and ML (2010s–Present)
The 2010s brought rapid progress in AI and Machine Learning (ML), revolutionizing CDSSs. AI-driven CDSSs now leverage vast datasets and sophisticated algorithms to offer personalized and accurate recommendations. Examples like IBM Watson Health and Google’s DeepMind showcase AI and ML’s transformative potential, akin to how AI is now enhancing precision and automation in china health care device parts tooling.
Mobile Health and Telemedicine (2010s–Present)
Mobile health (mHealth) and telemedicine expanded CDSS applications beyond traditional clinical settings. CDSS integration into mHealth apps and remote monitoring tools supports patients and providers outside hospitals, enabling proactive and personalized care, extending the reach of healthcare much like efficient logistics supported by china health care device parts tooling enable global distribution of manufactured goods.
Development of CDSS
The developmental trajectory of CDSS is deeply intertwined with advancements in AI, ML, and data analytics. Modern CDSSs, powered by robust ML algorithms, process extensive datasets and continuously refine their recommendations, ensuring relevance and actionability. This iterative improvement process mirrors the ongoing refinement of techniques and technologies in china health care device parts tooling to achieve greater precision and efficiency.
Research and development in CDSS should prioritize key areas to maximize healthcare impact:
-
Personalized Medicine: CDSS can significantly advance personalized medicine by tailoring treatments based on individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Integrating genomic and proteomic data enables clinicians to identify the most effective therapies, minimizing adverse effects. This personalized approach requires the same level of customization and precision found in specialized china health care device parts tooling for unique medical devices.
-
Predictive Analytics: Incorporating predictive analytics allows CDSS to anticipate potential complications and disease progression, facilitating early intervention and preventative care. Accurate outcome predictions based on patient data are crucial.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP advancements can unlock insights from unstructured clinical data in EHRs. Analyzing free-text clinical notes allows CDSS to provide more comprehensive and accurate recommendations.
-
Real-time Data Integration: Integrating real-time data from wearables and remote monitoring systems enables timely and actionable insights. This data informs treatment decisions and enhances patient monitoring.
-
Multi-modal Data Analysis: Analyzing multi-modal data, including medical imaging and lab results, provides a holistic patient view. CDSS capable of integrating diverse data sources are better equipped to support clinical decisions.
-
Advancements in AI and ML: Continued progress in AI and ML will further enhance CDSS capabilities. Advanced algorithms can process large data volumes more efficiently, improve recommendation accuracy, and identify previously unrecognized patterns. Future research should explore novel AI and ML methodologies for CDSS.
In essence, future CDSS development should focus on addressing current limitations, expanding applications, and adapting to new technologies and data sources. Collaboration and innovation are key to CDSS’s evolving role in healthcare.
Implementation and Integration
Implementing CDSS into healthcare systems is complex, demanding careful planning and execution, much like setting up a sophisticated manufacturing line that relies on china health care device parts tooling. A step-by-step guide to facilitate this process includes:
Assess the Needs and Goals
Before selecting a CDSS, healthcare organizations must define their specific needs and goals. Identifying areas where CDSS can have the greatest impact and determining desired outcomes is crucial.
Choose the Appropriate CDSS
Evaluate available CDSS solutions based on features, system compatibility, usability, and scalability. Select a system aligning with organizational needs, goals, and budget.
Assemble a Multidisciplinary Team
Form a team of clinical experts, IT professionals, and administrative staff to oversee implementation and integration. This team develops plans, sets timelines, and ensures project progression.
Develop a Comprehensive Plan
Create a detailed project plan with timelines, milestones, and success metrics. The plan should outline steps for successful CDSS implementation, including data migration, system configuration, training, and pilot testing.
Data Migration and Integration
Migrate patient data and integrate CDSS with EHR systems, ensuring seamless data exchange and interoperability. Collaboration with CDSS and EHR vendors is essential for proper integration and data security.
System Configuration and Customization
Configure CDSS to align with clinical workflows and preferences. Customize the system to accommodate unique needs, such as local guidelines and specific diagnostic criteria.
Training and Support
Provide comprehensive training to healthcare professionals using CDSS, including workshops and hands-on sessions. Establish a support system to address questions and concerns during implementation.
Pilot Testing
Conduct pilot tests to evaluate CDSS performance in a controlled setting. Use feedback from pilot tests to refine the system before full-scale implementation.
Full-Scale Implementation
Roll out CDSS across the organization, monitoring performance and impact on patient care. Continuously evaluate effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
Continuous Improvement and Evaluation
Regularly assess CDSS performance and gather user feedback to identify areas for improvement. Stay updated with advancements and incorporate new features to maintain system effectiveness.
Beyond these steps, successful CDSS integration necessitates understanding organizational culture and staff adaptability to change. Recognizing unique challenges in each healthcare setting, whether infrastructure, demographics, or practices, is vital. Just as china health care device parts tooling must adapt to different manufacturing environments, CDSS implementation needs to be context-sensitive.
Following these steps enables healthcare organizations to successfully implement and integrate CDSS. It is crucial to remember that CDSS augments, not replaces, human intuition and judgment. Synergy between human expertise and technology maximizes CDSS efficacy. Regular feedback from clinicians is invaluable for system refinement.
The future of CDSS will likely involve further AI and ML advancements. Staying attuned to these developments and addressing challenges will allow healthcare organizations to fully harness CDSS potential to enhance patient care and optimize healthcare delivery. Continuous updates, incorporating new research and integrating with newer technologies, are paramount for maintaining CDSS relevance and effectiveness.
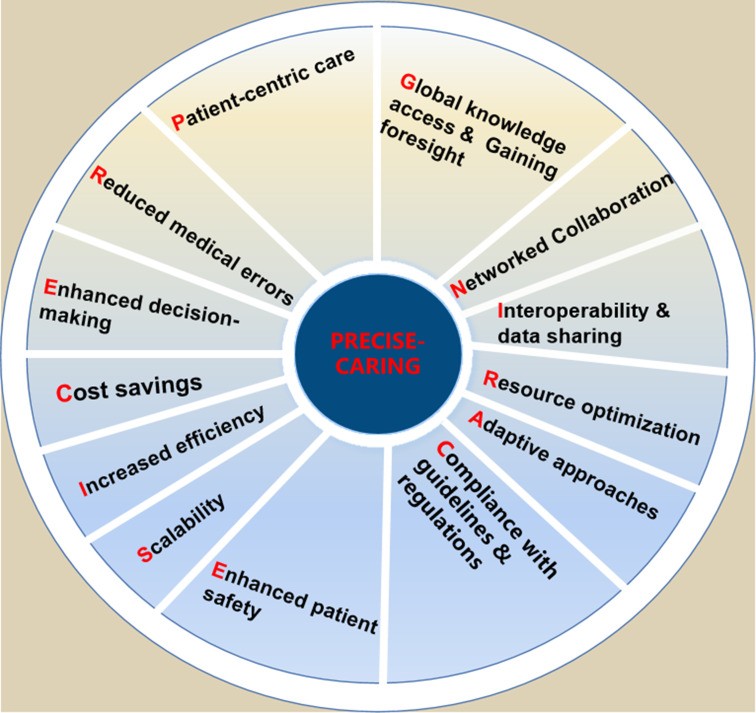
Benefits of CDSS (PRECISE-CARING)
CDSS is a vital health IT tool providing real-time clinical decision support to healthcare professionals. It aids in diagnosis, treatment, and care management using patient data, evidence-based guidelines, and best practices. CDSS improves patient outcomes by streamlining workflows, reducing mortality rates, and facilitating evidence-based decisions. It also enhances clinician satisfaction by providing real-time feedback and reducing cognitive burden. The numerous benefits of CDSS, encapsulated by the acronym PRECISE-CARING, are significant. Just as precision in china health care device parts tooling leads to higher quality products, precision in clinical decisions, facilitated by CDSS, leads to better patient outcomes.
PRECISE-CARING for the benefits of CDSS. CDSS, clinical decision support system.
- Patient-centric care: CDSS delivers personalized care with tailored treatment recommendations based on individual patient circumstances and history.
- Reduced medical errors: CDSS alerts and reminders for potential medication interactions, allergies, or contraindications prevent medical errors and enhance patient safety.
- Enhanced decision-making: CDSS assists healthcare providers in analyzing complex data, synthesizing information, and offering tailored suggestions, reducing cognitive overload and human error.
- Cost savings: CDSS identifies unnecessary tests, avoids duplicate procedures, and prevents complications, reducing healthcare costs. Accurate diagnoses and treatment plans further contribute to cost reduction.
- Increased efficiency: CDSS automates tasks and provides quick access to information, saving time for healthcare providers to focus on critical patient care aspects.
- Scalability: CDSS can be implemented across various healthcare settings, from large hospitals to small clinics, benefiting providers of all sizes.
- Enhanced patient safety: Reducing diagnostic errors and adverse drug events minimizes harm and improves overall patient safety.
- Compliance with guidelines and regulations: CDSS incorporates evidence-based guidelines, helping providers adhere to industry standards and avoid penalties.
- Adaptive approaches: CDSS enables personalized care by customizing treatment plans based on individual patient details.
- Resource optimization: CDSS streamlines tasks and automates processes, leading to efficient resource allocation and reduced manual work for healthcare professionals.
- Interoperability and data sharing: CDSS facilitates communication between healthcare systems, ensuring access to up-to-date patient information for clinical decisions.
- Networked collaboration: CDSS fosters better communication and cooperation among healthcare teams by centralizing data and providing a platform for shared insights.
- Global knowledge access and gaining foresight: CDSS serves as an educational resource, connecting professionals to the latest research and guidelines worldwide. It also aids in identifying at-risk patients for early interventions.
PRECISE-CARING underscores CDSS’s potential to revolutionize healthcare practices and significantly improve patient care quality and outcomes. This framework highlights how CDSS aids informed decisions, reduces errors, streamlines processes, and facilitates collaboration. It emphasizes adapting to patient needs, optimizing resources, and fostering continuous learning for evidence-based care.
CDSS also empowers patients by providing accessible information, enabling them to actively participate in their care. Furthermore, CDSS reduces practice variations, ensuring consistent, high-quality care regardless of the caregiver, much like standardized china health care device parts tooling ensures consistent product quality. By flagging deviations from best practices, CDSS promotes standardized yet personalized care. In the value-based care landscape, CDSS’s role in improving quality while reducing costs becomes more crucial, eliminating wasteful spending and optimizing resource use.
In summary, PRECISE-CARING highlights CDSS’s key benefits and clinical significance, underscoring their potential to revolutionize healthcare and enhance patient outcomes.
Evaluating the Impact of CDSS
Evaluating CDSS impact is crucial to determine their value and optimize performance. Rigorous evaluations measuring impact on patient outcomes, healthcare processes, and costs are essential. These evaluations should employ research designs like randomized controlled trials and cost-effectiveness analyses to inform decision-making and identify areas for improvement, similar to how performance testing and quality control are vital in validating the effectiveness of china health care device parts tooling.
As CDSS adoption increases, impact evaluation becomes more critical. The evaluation process is comprehensive, involving clinical effectiveness, user satisfaction, cost-effectiveness, and workflow integration, requiring both quantitative and qualitative methods.
Global variances in healthcare delivery are important to consider in evaluations. CDSS impact in a tertiary urban hospital may differ significantly from a rural primary care setting.
CDSS impact evaluation is ongoing, with healthcare organizations continuously monitoring performance and gathering user feedback for system refinement. While studies show positive effects, more research is needed on long-term impacts, healthcare costs, patient satisfaction, and overall care quality to build a stronger evidence base for CDSS implementation.
Global events like COVID-19 highlight the need for agility in CDSS evaluations, ensuring systems can rapidly incorporate new findings to equip providers with current information. Cybersecurity is also paramount in CDSS evaluation, ensuring resilience against threats and protecting patient data privacy.
In summary, CDSS impact evaluation focuses on evidence-based methodologies, data-driven analytics, data privacy, standardization, collaboration, and continuous improvement to ensure better patient care and outcomes.
Ethical Considerations
The growing use of CDSS raises ethical concerns related to algorithmic bias, transparency, and accountability. Future research must address these challenges by developing transparent and explainable algorithms, incorporating diverse patient populations, and establishing guidelines for responsible CDSS use. Ethical considerations are as crucial in CDSS development as quality and safety standards are in china health care device parts tooling.
Patient privacy, data security, and informed consent are critical ethical aspects requiring careful consideration as CDSS prevalence increases. Addressing these ethical challenges is crucial for building trust and ensuring responsible CDSS implementation.
Discussion
CDSS has shown significant potential to improve healthcare delivery, yet widespread adoption faces limitations. Overcoming these obstacles requires innovative solutions and sustained commitment from healthcare stakeholders.
This review has highlighted CDSS’s potential to improve patient outcomes, reduce errors, and enhance efficiency. The discussion covered history, development, implementation, benefits, and challenges.
While CDSS promises improved outcomes and reduced costs, implementation challenges cannot be ignored. A comprehensive approach addressing technical, organizational, and human factors is necessary.
CDSS’s potential to transform healthcare is substantial, but adoption challenges are significant. Addressing these challenges and harnessing opportunities will create more effective CDSS that improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. Future developments should focus on interoperability, transparent AI, user-centered design, continuous improvement, and collaboration.
Geographical Disparities in CDSS Implementation and Adherence
Geographical disparities significantly influence CDSS adoption and effectiveness. Publication bias favoring high-income, English-speaking countries can overshadow insights from diverse regions. Cultural nuances affect CDSS reception, with varying reliance on traditional practices versus technology. Training paradigms also differ, impacting clinician trust and adherence to CDSS recommendations. Addressing these geographical, cultural, and educational nuances is crucial for realizing CDSS’s global potential.
Challenges and Future Directions
Future research should focus on addressing CDSS limitations, improving system integration, and enhancing clinician acceptance. Long-term impact evaluations on patient outcomes, healthcare costs, and clinician satisfaction are needed. As CDSS evolves, it will play an increasingly vital role in shaping healthcare.
CDSS implementation challenges include technical, organizational, and human factors. Technical challenges involve data quality and interoperability, algorithm transparency, and system integration. Organizational challenges include resistance to change, financial constraints, and regulatory issues. Human factors involve user acceptance, usability, and training.
Data Privacy Concerns
Data privacy and security are critical concerns for CDSS. Ensuring patient information confidentiality and security is essential for building trust. Solutions include advanced encryption, strict access controls, and adherence to regulations like HIPAA.
Clinician Acceptance
Clinician acceptance is crucial for successful CDSS adoption. Enhancing acceptance requires user-friendly, relevant, and non-intrusive designs. Involving end-users in development ensures CDSS meets clinician needs and preferences.
Incorporating Patient Preferences and Values
Future CDSS research should incorporate patient preferences and values into decision-making. Integrating patient-reported outcomes and preferences supports shared decision-making and patient-centered care.
Expanding CDSS Applications to Underserved Populations and Settings
Expanding CDSS use to underserved populations and settings, like rural facilities and low-resource environments, is a future direction. Adaptable CDSS solutions can address healthcare disparities and broaden access to benefits.
System Integration
Integrating CDSS into clinical workflows and EHR systems is challenging. Innovative approaches to improve system integration include standardized data formats, service-oriented architectures, and user-centered design principles.
Training and Education
Adequate clinician training on CDSS use is essential for successful adoption. This includes understanding capabilities, limitations, and recommendation interpretation. Healthcare organizations should invest in training resources.
Tailoring CDSS to Local Contexts
Tailoring CDSS to local healthcare environments, including adapting to local guidelines and workflows, is crucial for user acceptance and integration. Customization enhances system relevance and effectiveness.
CAUCICETCI: Multifaceted Strategies for CDSS Advancement
Enhancing CDSS effectiveness involves multifaceted strategies, summarized by CAUCICETCI:
CAUCICETCI: multifaceted strategies for CDSS advancement. AI, artificial intelligence; CDSS, clinical decision support system; EHRs, electronic health records.
- Customisability: Tailoring CDSS to unique clinical contexts and user preferences.
- Addressing ethical and legal concerns (responsibility): Ensuring responsible use regarding data privacy, consent, and liability.
- User-centred design: Designing intuitive and easy-to-use CDSS to reduce clinician cognitive burden.
- Collaboration: Fostering multi-disciplinary collaboration between healthcare professionals, developers, and data scientists.
- Integration with EHRs: Improving data exchange, interoperability, and security between CDSS and EHRs.
- Continuous updates and knowledge expansion: Efficiently incorporating the latest medical research and best practices.
- Evaluation and feedback mechanisms: Assessing impact on outcomes, satisfaction, and cost-effectiveness for system improvement.
- Transparent and explainable AI: Providing clear reasoning behind recommendations to build trust and acceptance.
- Continuous improvement: Using feedback loops and performance metrics for ongoing system refinement.
- Interoperability and standardisation: Ensuring seamless integration through standardized data formats.
CAUCICETCI highlights key opportunities to enhance CDSS effectiveness, including seamless EHR integration, interoperability, AI/ML leverage, continuous updates, user-friendly interfaces, customizability, evaluation, ethics, and stakeholder engagement. Focusing on these areas ensures CDSS remains a valuable tool for improving clinical decisions and patient care. Just as continuous improvement and innovation are essential in china health care device parts tooling to maintain competitiveness and quality, these strategies are vital for CDSS to reach its full potential.
Future Directions
As technology evolves, CDSS potential in healthcare will grow. Future AI and ML advancements can further enhance diagnostic and predictive capabilities. Expanding CDSS applications to underserved populations can address healthcare disparities. Collaborative efforts among stakeholders are crucial to realize CDSS’s full potential.
Conclusion
This review has provided a comprehensive overview of CDSS, examining development, implementation, benefits, limitations, and future directions. We discussed challenges in data privacy, system integration, clinician acceptance, patient preferences, underserved populations, and training. We also explored opportunities to enhance CDSS effectiveness through EHR integration, interoperability, AI/ML, updates, user-friendly design, customization, and evaluation.
In conclusion, harnessing CDSS power requires a multifaceted approach addressing implementation barriers and optimizing effectiveness. Considering ethical aspects, ensuring seamless integration, promoting clinician acceptance, focusing on continuous improvement, and fostering collaboration will make CDSS a powerful tool for transforming patient care and improving healthcare outcomes. The precision and continuous improvement sought in fields like china health care device parts tooling are equally crucial for the successful evolution and widespread adoption of CDSS in healthcare.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and improvement suggestions that further led us to improve this paper.
Footnotes
ZC and NL contributed equally.
Contributors: ZC, YW and NS conceived and designed this review. ZC, HZ, HL and YY did the search. XZ and YC selected the studies for inclusion. ZC and NL drafted the manuscript. ZC, HZ and HL edited and approved the final version.
Funding: We thanked the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences Independent Selection Project (Z0830) and Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine Independent Selection Project, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences Independent Selection Project (Z0830-1) for their support for this work.
Competing interests: None declared.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data availability statement
No data are available.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
References
Associated Data
Data Availability Statement
No data are available.