Data is the lifeblood of modern decision-making, and this is especially true in the rapidly evolving healthcare sector. The ability to leverage data effectively is no longer a luxury but a necessity for healthcare organizations aiming to improve patient outcomes, streamline operations, and ensure financial stability. The global predictive analytics market is projected to reach $22 billion by 2026, highlighting the increasing importance of data-driven strategies across industries, and healthcare is at the forefront of this transformation.
The healthcare industry is awash in data. From electronic health records (EHRs) and wearable devices to insurance claims and population health statistics, the volume of information is staggering. It’s estimated that patients generate around 80MB of data annually, and this number is only growing. This vast data landscape presents a significant opportunity for healthcare organizations to move beyond traditional, intuition-based decision-making and embrace a more data-driven approach. To effectively harness this data, healthcare organizations need the right data-driven health care organization tools.
Applied data analytics can revolutionize healthcare. It empowers organizations to enhance medical care, optimize administrative processes, reduce costs, mitigate staff burnout, and ultimately improve patient experiences. Hospitals and healthcare systems are increasingly relying on data analysis and predictive modeling to make informed, evidence-based decisions and strategies.
Understanding Data-Driven Decision-Making (DDDM) in Healthcare
Data-driven decision-making (DDDM) in healthcare involves utilizing information that has been meticulously collected, modeled, and analyzed to gain deep insights into specific challenges and develop effective solutions. For DDDM to be successful, the data must be reliable, accurate, valuable, and relevant. This means data needs to be timely, cleansed of errors, and directly applicable to the healthcare questions and objectives at hand. The core objective of DDDM is to eliminate guesswork and subjectivity from decision-making processes in healthcare.
Healthcare organizations that embrace DDDM and utilize data-driven health care organization tools often experience significant improvements in efficiency and overall performance.
The advantages of data-driven decision-making in healthcare are numerous:
However, to fully realize these benefits, healthcare leaders must possess a comprehensive understanding of DDDM principles and the capabilities of the tools they employ. Potential pitfalls of DDDM include:
Key Types of Data Analytics Tools in Healthcare
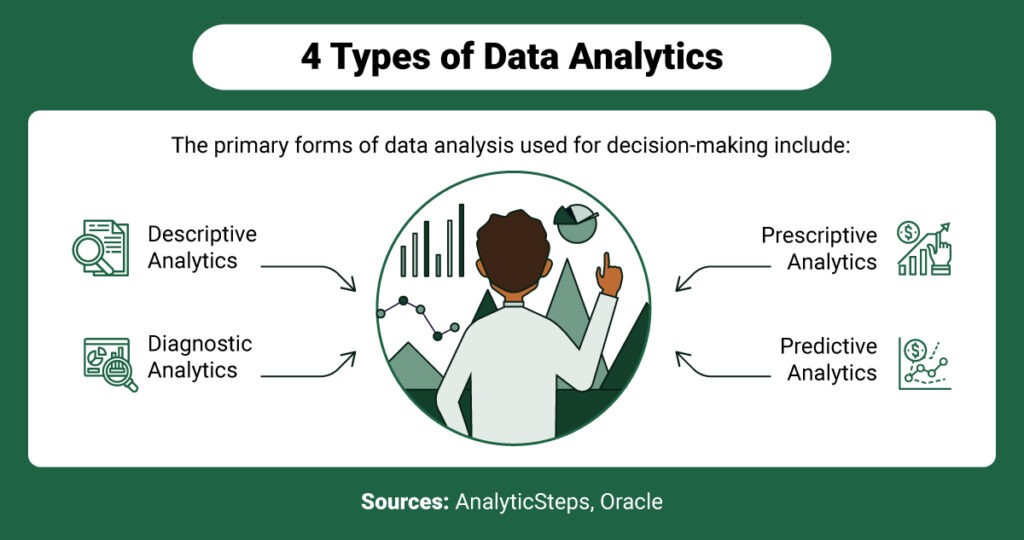
To effectively implement DDDM, healthcare organizations leverage various types of data analytics, each requiring specific data-driven health care organization tools. These can be broadly categorized into four main types:
Descriptive Analytics Tools
Descriptive analytics tools focus on understanding past trends and behaviors. In healthcare, these tools help to analyze historical patient data to understand what has happened.
Examples of descriptive analytics in healthcare include analyzing:
- Patient demographics and visit patterns
- Prescription trends and medication adherence
- Surgical outcomes and treatment effectiveness
- Financial data, billing patterns, and geographic data for population health insights
Data-driven health care organization tools for descriptive analytics often include reporting dashboards, data visualization software, and EHR analysis tools. These tools present historical data in an understandable format, enabling healthcare professionals to identify trends and patterns.
Diagnostic Analytics Tools
Diagnostic analytics tools go beyond describing what happened and delve into understanding why it happened. In healthcare, diagnostic analytics, sometimes called root cause analysis, helps to understand the underlying reasons for specific outcomes or trends.
Data-driven health care organization tools for diagnostic analytics are often more sophisticated and may include:
- AI-powered analytics platforms: These platforms can process large datasets from EHRs, medical imaging, and research literature to identify correlations and potential causes of medical conditions or operational inefficiencies.
- Statistical analysis software: Tools like SAS, R, and SPSS are used to perform in-depth statistical analysis to uncover relationships and dependencies in healthcare data.
- Data mining tools: These tools help to discover hidden patterns and anomalies in large datasets, which can be crucial for understanding the root causes of healthcare issues.
For example, in healthcare, diagnostic analytics can be used to understand why a hospital’s readmission rates are higher than average or why certain patient populations are experiencing poorer health outcomes. AI-powered tools can analyze vast quantities of patient data, research papers, and clinical guidelines to pinpoint contributing factors.
Predictive Analytics Tools
Predictive analytics utilizes historical and current data to forecast future outcomes and trends. In healthcare, this is invaluable for anticipating patient needs, predicting disease outbreaks, and proactively managing resources.
Data-driven health care organization tools for predictive analytics are crucial for proactive healthcare management:
- Machine learning platforms: These platforms build predictive models based on healthcare data to forecast patient risks, predict hospital admissions, and estimate resource needs.
- Predictive modeling software: Tools that enable data scientists to build and deploy predictive models for various healthcare applications, such as disease prediction and risk stratification.
- Real-time analytics dashboards: These dashboards display predictive insights in real-time, enabling healthcare providers to make timely interventions.
Examples of predictive analytics in healthcare include predicting patient no-show rates, forecasting demand for hospital beds, identifying patients at high risk of developing certain conditions, and predicting the likelihood of disease outbreaks.
Prescriptive Analytics Tools
Prescriptive analytics tools go a step further than predictive analytics by recommending the best course of action based on data-driven insights. In healthcare, prescriptive analytics helps to optimize decisions related to treatment plans, resource allocation, and operational improvements.
Data-driven health care organization tools for prescriptive analytics are designed to guide decision-making:
- Clinical decision support systems (CDSS): These systems integrate patient data with clinical guidelines and best practices to provide clinicians with evidence-based recommendations at the point of care.
- Optimization algorithms: These algorithms analyze healthcare data to identify optimal solutions for resource allocation, staffing levels, and treatment pathways.
- Simulation software: Tools that allow healthcare organizations to simulate different scenarios and evaluate the potential impact of various decisions before implementation.
For example, prescriptive analytics can help determine the most effective treatment plan for a patient based on their individual characteristics and medical history, optimize staffing levels in a hospital based on predicted patient volumes, or recommend optimal dosages for radiation therapy.
Essential Data Analytics Tools for Healthcare Organizations
Beyond the specific types of analytics, several categories of data-driven health care organization tools are essential for building a robust data-driven infrastructure.
Data Science Tools
Data scientists are at the heart of data-driven healthcare. They use specialized tools to manage, model, and analyze complex healthcare datasets.
Common data science tools include:
- Programming languages: Python and R are widely used for data manipulation, statistical analysis, and machine learning.
- Statistical software: SAS, SPSS, and MATLAB are powerful tools for advanced statistical modeling and analysis.
- Big data platforms: Hadoop and Spark are used to process and analyze massive datasets that are common in healthcare.
- Cloud-based data science platforms: Platforms like Google Cloud AI Platform, AWS SageMaker, and Azure Machine Learning provide scalable and collaborative environments for data science projects.
Interactive Dashboards and Data Visualization Tools
For data insights to be actionable, they need to be easily understood by healthcare professionals across different roles. Interactive dashboards and data visualization tools are critical for this purpose.
Key features of these tools include:
- Real-time data updates: Dashboards should display up-to-date information to enable timely decision-making.
- Customizable visualizations: Tools should allow users to create various types of charts, graphs, and maps to visualize data effectively.
- Interactive exploration: Users should be able to drill down into data, filter information, and explore different dimensions to gain deeper insights.
- Alerts and notifications: Dashboards can be configured to trigger alerts when key metrics deviate from expected ranges.
Examples of popular data visualization tools include Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik Sense.
Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
Business intelligence (BI) tools in healthcare focus on leveraging data analytics to improve an organization’s overall business performance. These tools integrate data from various sources, including clinical, financial, and operational systems, to provide a holistic view of the organization’s health.
Healthcare BI tools typically offer features such as:
- Data warehousing: Centralizing data from disparate sources into a unified repository for analysis.
- Reporting and analysis: Generating reports and performing ad-hoc analysis to track key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Performance dashboards: Visualizing organizational performance across different dimensions.
- Benchmarking: Comparing performance against industry benchmarks and peer organizations.
Healthcare BI tools help organizations identify areas for improvement in financial performance, operational efficiency, and patient outcomes.
Implementing Data-Driven Strategies in Healthcare
To successfully implement data-driven decision-making, healthcare organizations need to adopt a strategic approach that encompasses not only technology but also culture and processes.
Key strategies include:
- Data Quality and Governance: Establish robust data quality processes to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Implement data governance frameworks to manage data access, security, and compliance.
- Investing in Technology and Infrastructure: Adopt the right data-driven health care organization tools and infrastructure to support data collection, storage, processing, and analysis. This may include investing in EHR systems, data warehouses, analytics platforms, and data visualization tools.
- Building Data Analytics Capabilities: Develop in-house data analytics expertise by hiring data scientists, analysts, and engineers. Provide training to existing staff to enhance their data literacy and analytical skills.
- Fostering a Data-Driven Culture: Promote a culture that values data-driven insights and encourages evidence-based decision-making at all levels of the organization.
- Engaging Stakeholders: Involve clinicians, administrators, and other stakeholders in the DDDM process to ensure that data-driven initiatives are aligned with organizational goals and address real-world needs.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: The Future of Healthcare
Data-driven decision-making is fundamentally transforming healthcare. By leveraging the power of data-driven health care organization tools, healthcare providers can move beyond intuition and make informed decisions that lead to improved patient care, enhanced operational efficiency, and a more sustainable healthcare system. As data volumes continue to grow and analytics technologies advance, the role of DDDM in healthcare will only become more critical. Organizations that embrace data-driven strategies and invest in the necessary tools and capabilities will be best positioned to thrive in the evolving healthcare landscape and deliver better outcomes for patients and communities.
Infographic Sources:
Analytics Steps, “What Is Data Analytics and Its Types?”
Built In, “11 Big Data in Healthcare Applications and Examples”
Datapine, “21 Examples of Big Data Analytics in Healthcare That Can Save People”