During public health education, students learn numerous epidemiological and statistical formulas, often initially calculated manually before transitioning to computer software. Several commercial programs, such as SAS®, SPSS®, and Stata®, are commonly taught in schools of public health (SPHs) and are widely used in epidemiology due to their power. 1 However, these programs present limitations in resource-constrained settings: they can be expensive, complex to learn, have significant hardware requirements, and may lack readily available user support.
To address these limitations, free epidemiologic programs like Epi Info (www.cdc.gov/epiinfo) and EpiData (www.epidata.dk) are available. Yet, even some of these programs may not include all epidemiologic parameters and statistical calculations needed in SPH courses. Recognizing these gaps, a program was developed to better support the teaching of epidemiologic and statistical methods: OpenEpi.
Introducing OpenEpi: A Web-Based Solution for Health Data Analysis
OpenEpi (www.OpenEpi.com) stands out as a free, web-based, open-source suite of programs designed for public health and medicine. It serves as an invaluable tool for both training and practical application, offering a range of epidemiologic and statistical tools for summary data. 2–7 Built using JavaScript and HTML, OpenEpi is compatible with various web browsers like Microsoft® Explorer, Firefox®, Safari, and Opera, and operates across different systems including Windows, Macintosh, and Linux, even extending to mobile use on devices like iPhones. Users can access OpenEpi directly from its website or download it for offline use. Its source code and documentation are openly accessible, encouraging further development and adaptation. Currently, OpenEpi supports English, French, Italian, and Spanish languages, enhancing its global accessibility.
The developers of OpenEpi bring extensive experience from their involvement with Epi Info, a program from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) widely used for data entry and analysis. OpenEpi was conceived to replicate and enhance the analyses found in Epi Info’s DOS-based modules, StatCalc and EpiTable, and to introduce tools and calculations not yet available in Epi Info. It represents a significant stride towards a comprehensive, web-based collection of epidemiologic software tools, designed to complement programs like Epi Info, SAS, SPSS, Stata, and EpiData, particularly in regions with limited resources.
Initial funding for OpenEpi came from a grant from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation to Emory University. Since its inception in 2003, OpenEpi has recorded over 1.4 million accesses from 160 countries, with nearly 500,000 in the first half of 2008 alone. A recent Google search identified almost 5,000 websites referencing OpenEpi, highlighting its growing recognition and utility in the global health community.
Analytic Capabilities of OpenEpi for Healthcare Professionals
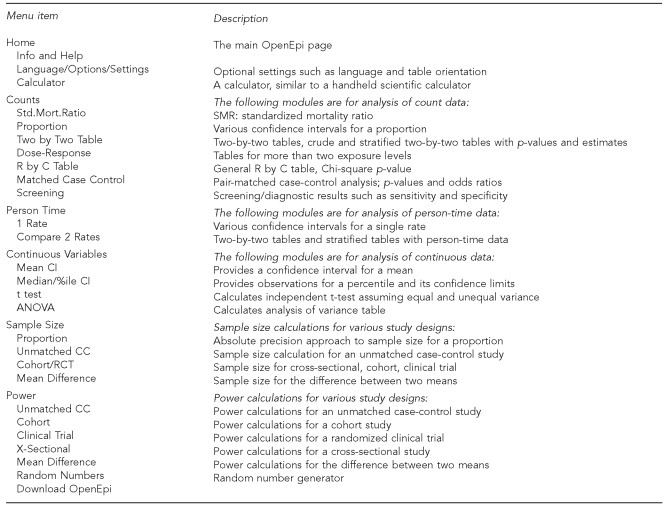
OpenEpi provides a robust set of calculations essential for epidemiologic analysis and health research, as illustrated in Figure 1. These capabilities include:
- Confidence intervals for proportions, rates, standard mortality ratio, mean, median, and percentiles.
- Two-by-two contingency tables for both crude and stratified count and rate data.
- Matched case-control study analysis.
- Trend tests for count data.
- Independent t-tests and one-way ANOVA.
- Diagnostic and screening test evaluations, including ROC curve analysis.
- Sample size calculations for proportions, cross-sectional studies, case-control studies (unmatched), cohort studies, randomized controlled trials, and comparisons of two means.
- Power calculations for proportions (in case-control, cross-sectional, cohort, and clinical trials) and for comparing two means.
- Random number generation.
For epidemiologists and health researchers, OpenEpi excels in calculations based on cross-tabulations, going beyond what is offered by many standard statistical programs. For a single two-by-two table, OpenEpi not only delivers conventional results but also estimates:
- Etiologic and prevented fraction in the population and among the exposed, with confidence intervals, based on risk, odds, or rate data.
- Cross-product and maximum likelihood odds ratio estimates.
- Mid-p, exact p-values, and confidence limits for the odds ratio.
- Rate ratios and rate differences with confidence intervals and statistical tests.
Analyzing stratified two-by-two tables with count data, OpenEpi calculates:
- Mantel-Haenszel and precision-based risk ratio and odds ratio estimates.
- Precision-based adjusted risk difference.
- Interaction tests for risk ratio, odds ratio, and risk difference.
- Four distinct confidence limit methods for the odds ratio.
Similar to Epi Info, OpenEpi presents both crude and adjusted estimates in stratified analyses, facilitating the assessment of confounding. For rate data, it provides adjusted rate ratios and rate differences, along with interaction tests. Furthermore, for count data, OpenEpi conducts trend tests for both crude and stratified data, offering a comprehensive suite of analytical tools for healthcare data.
Each OpenEpi module is designed for user-friendliness, exemplified by the module interface shown in Figure 2, which includes five key tabs. The “Start” tab offers a module overview, while the “Enter” tab is for data input, with an “Enter New Data” button for direct data entry. Calculation results are found under the “Results” tab, and practical examples are available in the “Examples” tab. The “Help” tab provides immediate assistance for program-related queries. Additional links for “Documentation” detail the analytic methods and formulas used, and “Testing” compares OpenEpi results with other software and textbook examples. Many modules also feature a “Load Demo Data” button, simplifying the initial use by pre-populating example datasets.
Example of “Start” page for two-by-two table module
OpenEpi’s Role in Epidemiology and Public Health Education
OpenEpi has been effectively integrated into the curricula of numerous institutions, including Columbia University, Emory University, Morehouse College, San Jose State University, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, University of Michigan, and University of Wisconsin, across both on-campus and remote learning programs. Its ease of use, elimination of programming requirements, and web-based accessibility allow students to concentrate on interpreting results, making it an excellent pedagogical tool for epidemiology and public health.
Future Enhancements for OpenEpi Data Software
Looking ahead, the developers aim to further enhance OpenEpi through several key improvements: (1) refining existing programs, (2) adding new programs for epidemiologic, statistical, and nutritional analyses, (3) enabling data import via cut and paste, (4) expanding language support, and (5) broadening global awareness and utilization of OpenEpi. Prototype modules for advanced analyses like logistic regression and survival analysis are currently accessible. The developers encourage community contributions in developing and testing new modules, fostering the growth and utility of OpenEpi as a vital resource for healthcare data analysis and public health research.